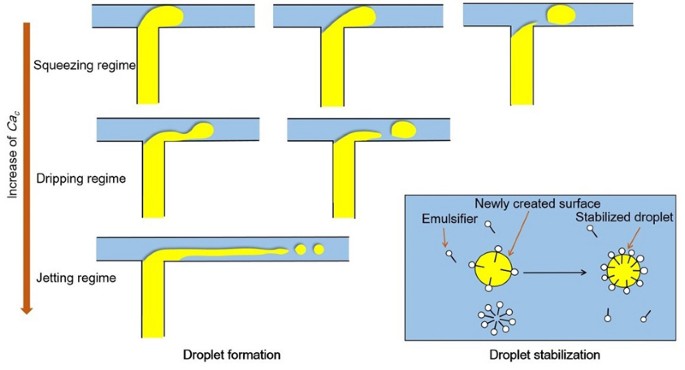
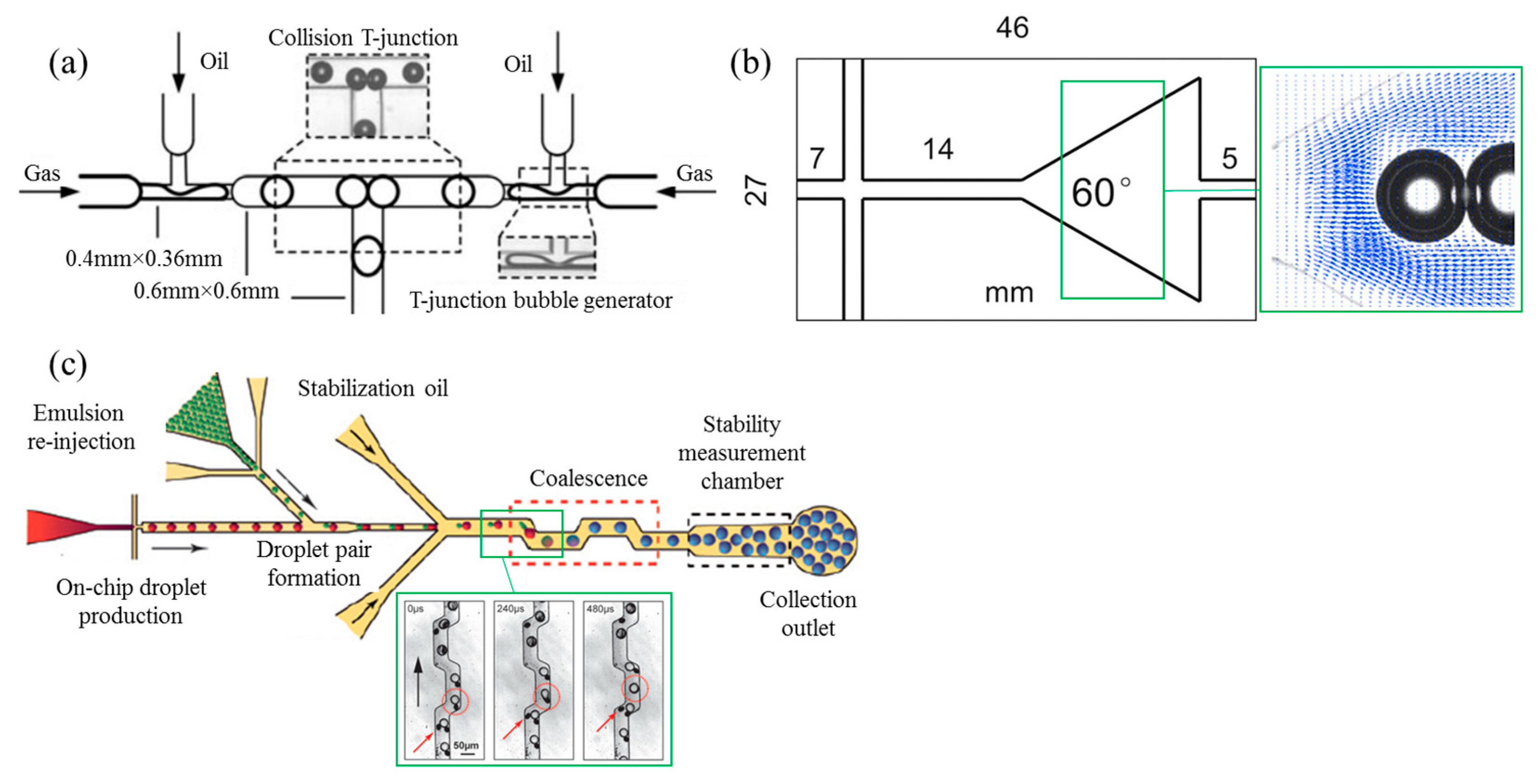
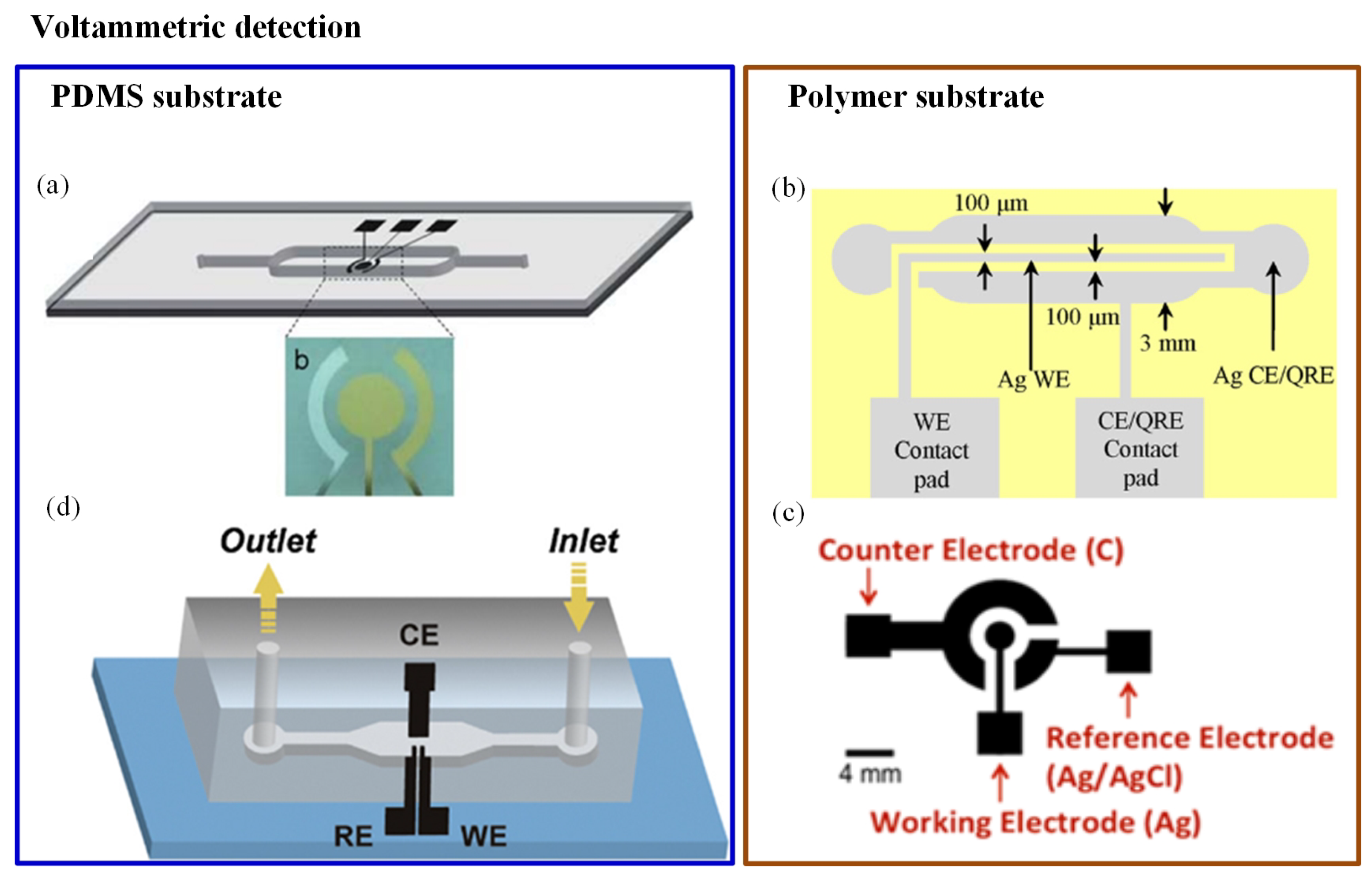
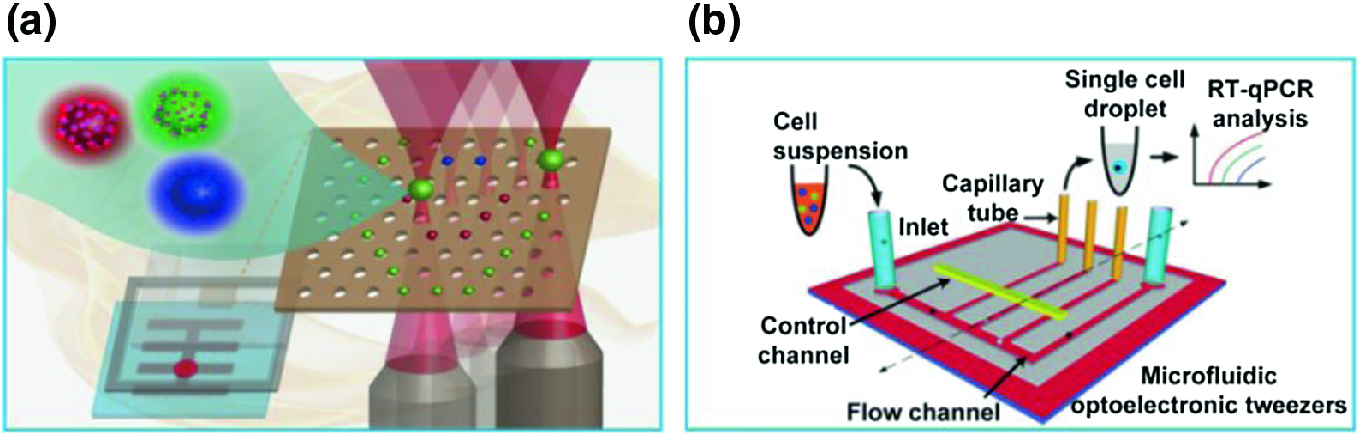
The conventional microfluidic fuel cell requires maintenance of a co laminar flow thereby imposing creep flow which is not necessary in paper based devices 4.
Microfluidic co laminar flow cell.
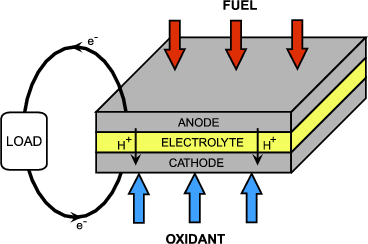
This communication reports the design and characterization of an air breathing laminar flow based microfluidic fuel cell lffc.
This study focuses on developing a mathematical model for the electrochemical reduction of co 2 into ch 3 oh in a microfluidic flow cell.
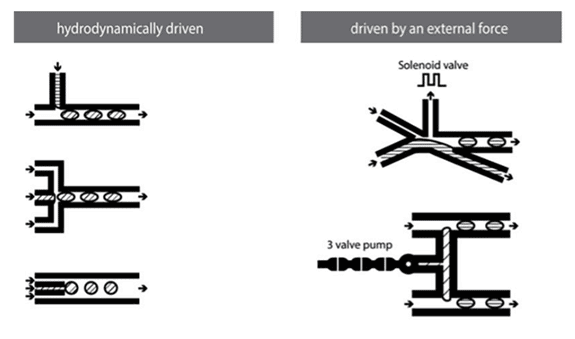
Flow cytometry is a common technique for counting and sorting cells detecting bio markers and for cell manipulation and imaging.
A woven thread based microfluidic fuel cell based on graphite rod electrodes is proposed.
With this design.
The performance of previous lffc designs was cathode limited due to the poor solubility and slow transport of oxygen in aqueous media.
Therefore no external pumps are required to maintain the co laminar flow benefiting for the integration and miniaturization.
This can be done with a flow cytometer or with microfluidic flow cells.
The present work is the first attempt to model the electro reduction of co 2 to alcohols which is a step forward toward the scale up of the process to industrial operation.
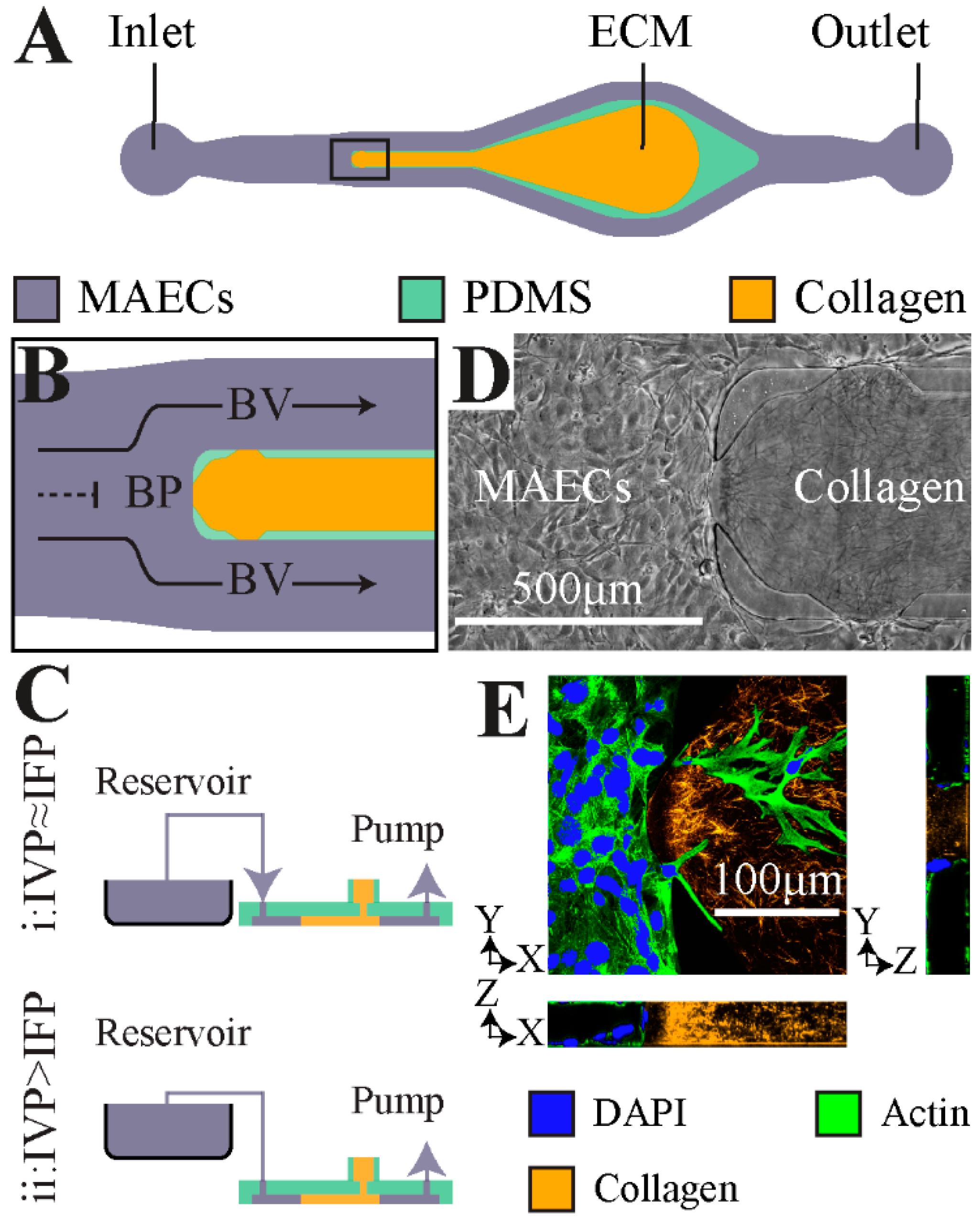
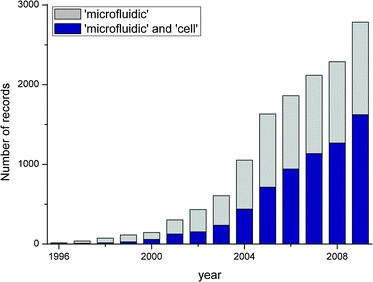
Microfluidic cell culture integrates knowledge from biology biochemistry engineering and physics to develop devices and techniques for culturing maintaining analyzing and experimenting with cells at the microscale.
3 although the microfluidic channels are square or rectangular the cross sections of the caa microfiber remain circular or elliptic.
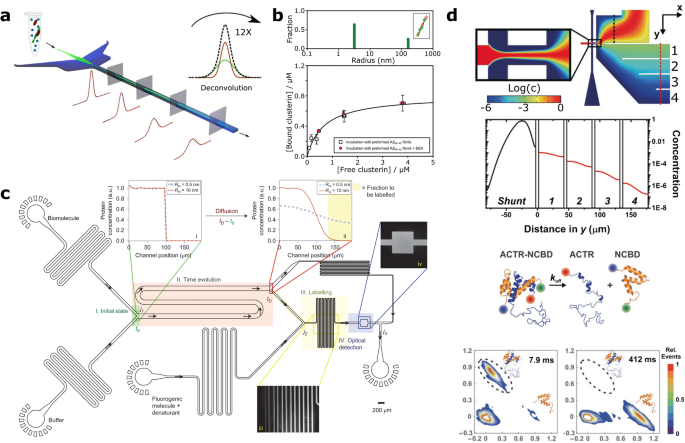
U flux is an integrated solution to reliably perform single molecule experiments in a laminar flow environment.
A flow cell is an excellent tool for these purposes because of its capillary channels and optical characteristics.
It is a multidisciplinary field that involves engineering physics chemistry biochemistry nanotechnology and biotechnology it has practical applications in the design of.
Microfluidics refers to the behaviour precise control and manipulation of fluids that are geometrically constrained to a small scale typically sub millimeter at which capillary penetration governs mass transport.
Individual half cells based on either alkaline borohydride or acidic peroxide might however find some application in a cell architecture that accommodates low rates of gas evolution such as the previously described grooved.
Both inter fiber gaps and inter weave spaces could provide flow channels for the liquid transport through the woven cotton thread.
It merges microfluidics a set of technologies used for the manipulation of small fluid volumes μl nl pl within artificially fabricated microsystems and cell culture.
The model features a simple.
Introduction of an air breathing gas diffusion electrode as the cathode addresses these mass transfer issues.
Unlike the conventional.